
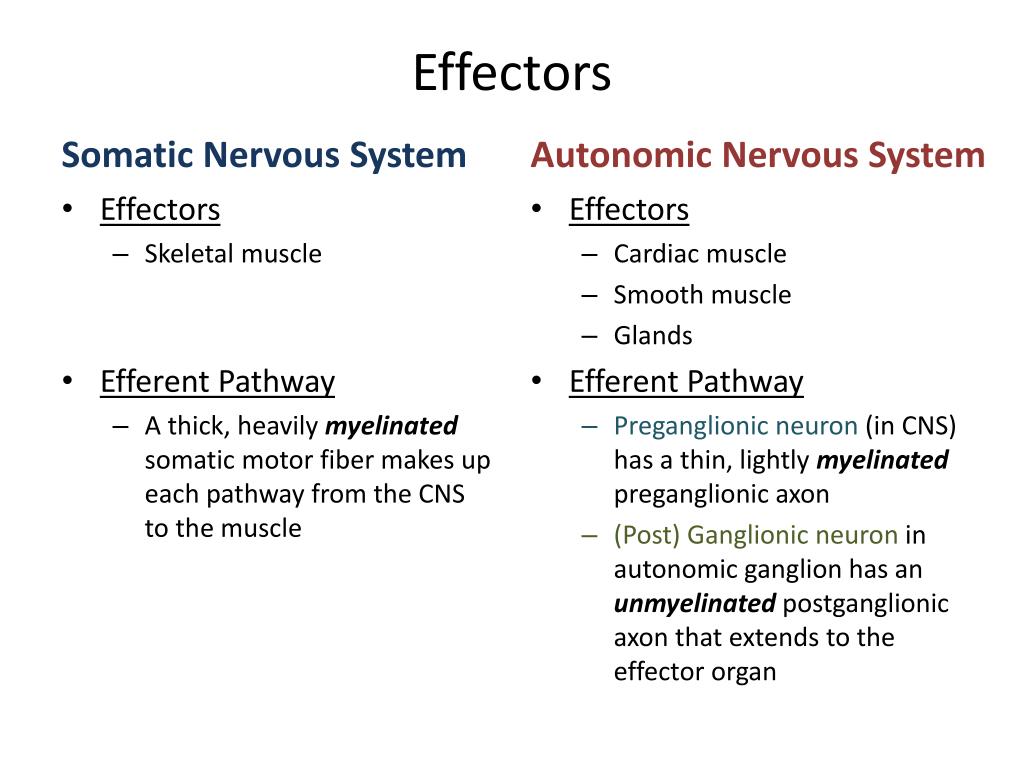
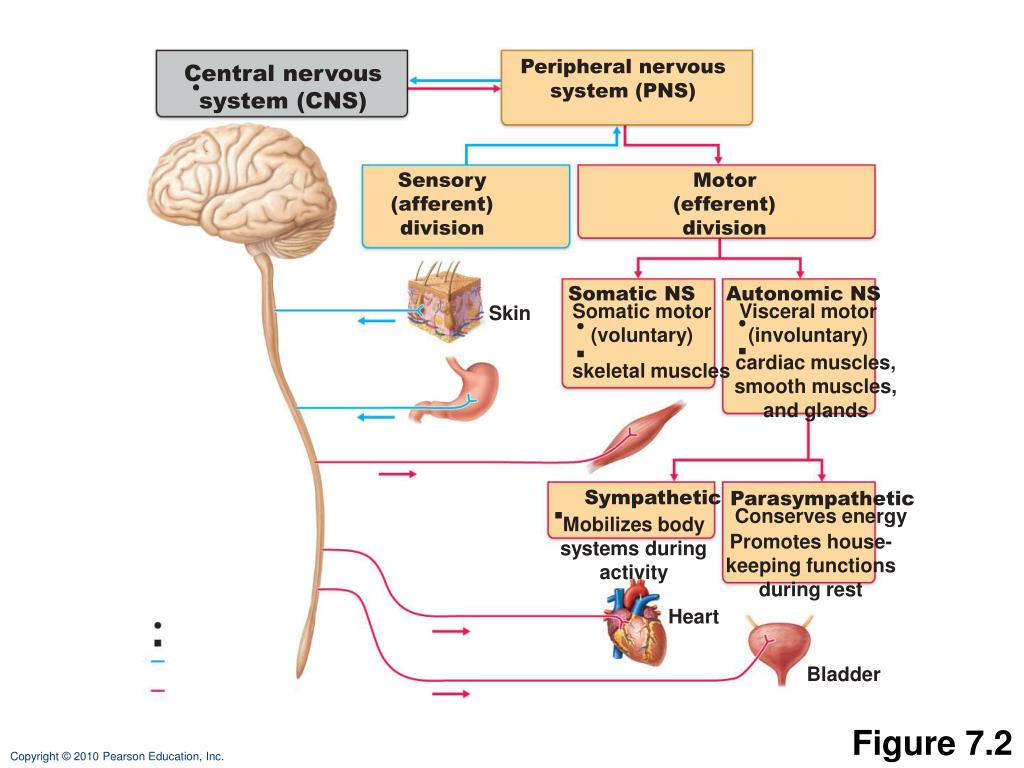

Some nerve fibers that connect with autonomic effectors also pass through the ventral roots of the spinal nerves by way of a ganglion located outside the spinal cord and are then distributed to smooth muscles and glands. Glandular secretions controlled by autonomic effectors include external secretions, such as sweat, and internal ones, such as the hormone epinephrine secreted by the adrenal medulla of the brain. The smooth muscles that are supplied by these effectors maintain the tone of blood vessels walls, thus helping to regulate blood pressure. The autonomic effectors receive impulses from the lateral part of the gray matter. It consists of neurons that are associated with skeletal or striated muscle fibers and influence voluntary movements of the body. The postganglionic neurons give off long axons (postganglionic fibers) that leave the ganglia and project onto visceral effectors, where they release the. On the other hand, autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary movements of internal organs. The somatic nervous system (SoNS), also known as the voluntary nervous system, is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The somatic effectors, which are responsible for powerful motor movements, are linked to the ventral horn cell, a large neuron in the ventral portion of the gray matter. Somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate. motor (or effector or efferent) neurones transmit impulses from CNS to muscles and glands. Central (CNS): brain and spinal cord Peripheral (PNS): spinal and cranial nerves which include the following - somatic nervous system deals with skeletal. The muscles are generally divided into two groupings: somatic effectors, which are the body's striated muscles (such as those found in the arm and back), and autonomic effectors, which are smooth muscles (such as the iris of the eye).īoth types of effectors are linked to the gray matter of the spinal cord, but each system originates in a different portion of it. The PNS is divided into the somatic system that coordinates. Finally, some nerves are mixed nerves that contain both afferent and efferent axons. Other neurons, known as efferent nerves, carry signals only from the central nervous system to effectors such as muscles and glands. In humans, effectors may either be muscles, which contract in response to neural stimuli, or glands, which produce secretions. The somatic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of the body movements via the use of. Nerves that carry information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system only are called afferent nerves. Peripheral tissue at the outer end of an efferent neural path (one leading away from the central nervous system).Īn effector acts in special ways in response to a nerve impulse.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
